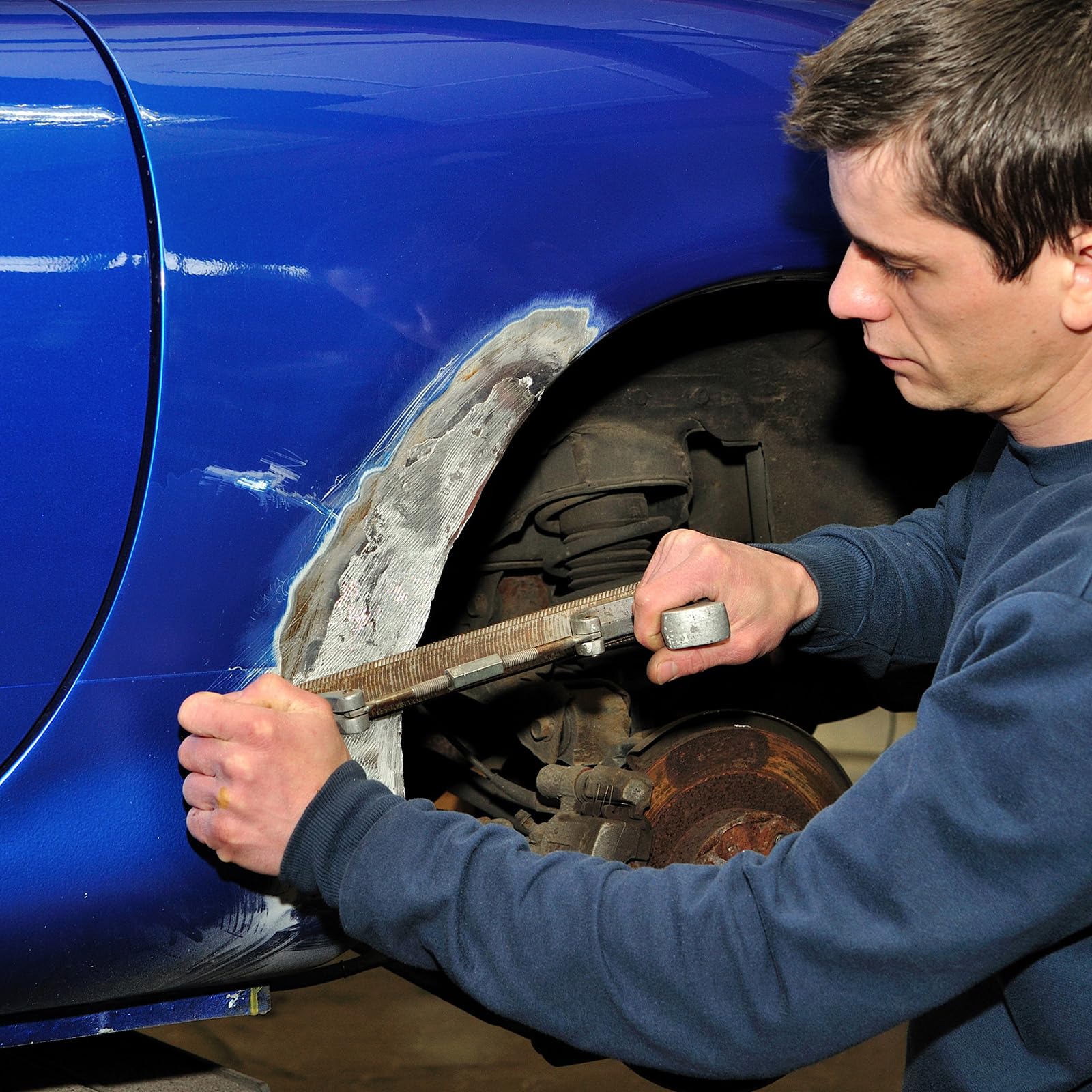
Double Holes Aluminum Files | Flat Flexible Curved Tooth Files
Premium quality double holes aluminum file, aluminium files, flat double cut aluminum files, files for aluminum sharping.
| Item No.: | CS1511 |
| Material: | High Carbon Steel |
| Handles: | Two-component plastic handle |
| Size: | 12", 14" |
| Cuts: | Bastard Cut |
| Packaging: | Blister Card |
Detailed Description:
Chinese professional manufacturer of half round aluminum files.
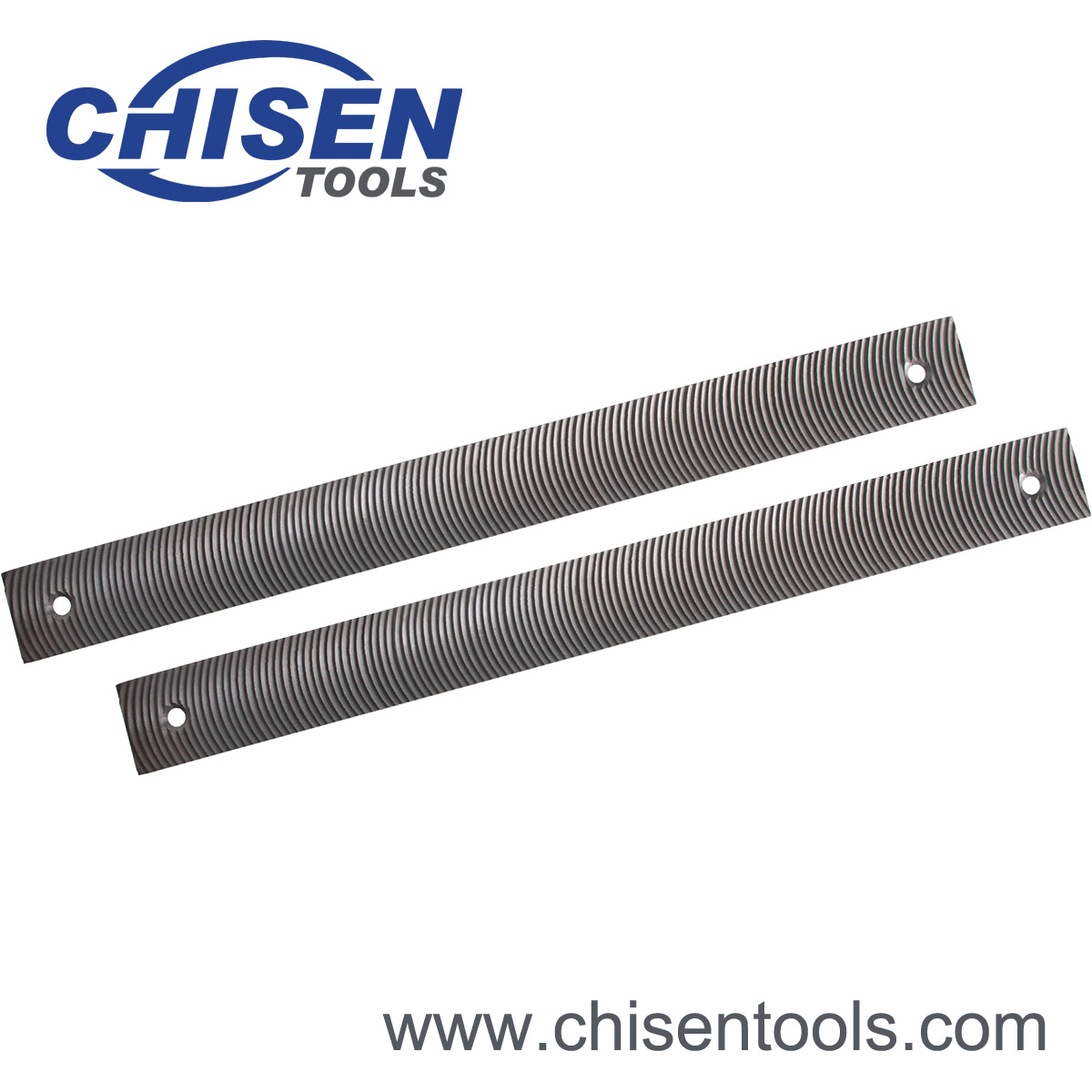

Double Holes Aluminum Files' Features
Double Holes Aluminum Files, also know as Flat Flexible (Blade) Curved Tooth Files, are designed for smooth, scratch-free work on all types of auto body and sheet metal work and where filing has to be done in the middle of large surfaces. Flexible blades have teeth on both sides and can be adjusted to file outward (convex) and inward (concave) or flat.| Item No. | Size | Type of Cut | QTY(pcs)/CTN | Dimension of Carton(cm) | G.W./N.W.(kgs) |
| CS1511112 | 12" | Bastard Cut | 60 | 41*22*12 | 24/23 |
| CS1511114 | 14" | Bastard Cut | 60 | 46*23*12 | 30/29 |
What are aluminum files?
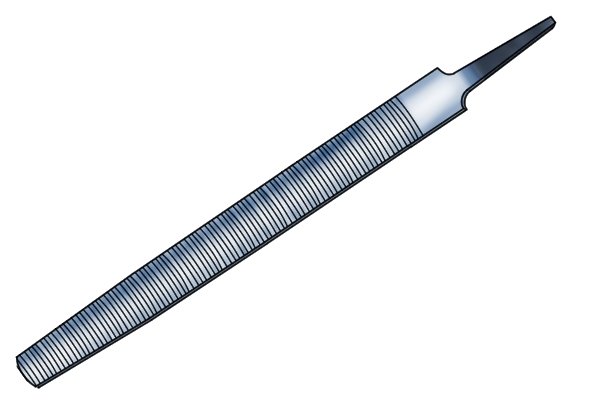
Aluminium files are special tools that have been developed for the shaping, finishing and deburring of aluminium without causing the file to clog. Milleni cut files can also be used on aluminium as they feature a straight tooth cut diagonally on the blade that also prevents clogging.
Why does aluminium clog files?
Aluminium is a soft metal.
When a file’s teeth drag across aluminium, the soft chips that are shorn off can curl into the teeth of the file and become stuck. This is known as ‘pinning’.
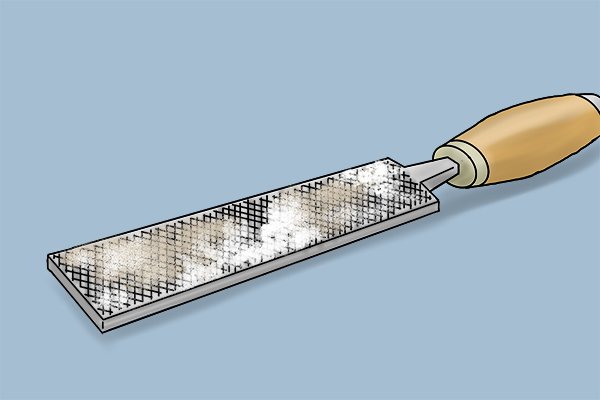
Why is pinning a bad thing?
If a chunk of jammed debris gets big enough, it can start to scratch the surface of your workpiece. If you’re filing to create a beautiful finish then this can be a bit of a problem!What are the characteristics of aluminium files?
Cross section and profile
Aluminium files have a rectangular cross section and are slightly tapered in width and thickness.Cut
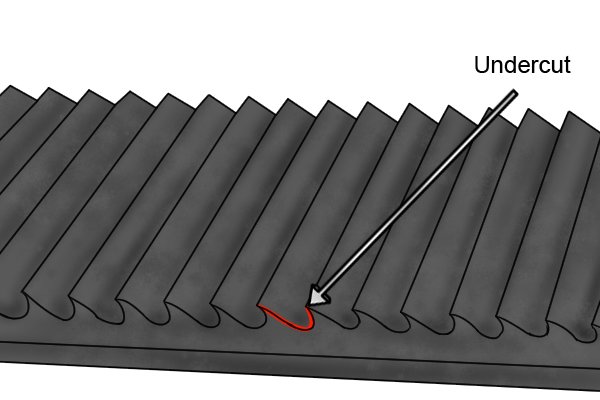
The teeth on aluminium files are ‘undercut’ – in other words, there is more space between the tip of the tooth and the file body. This makes it much more difficult for debris to get jammed, because the space beneath the teeth is too large.
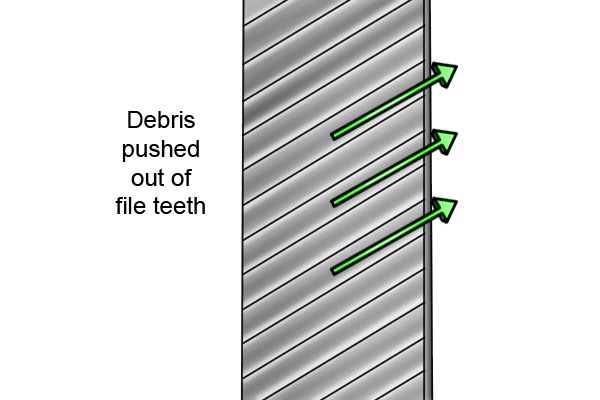
Even if the teeth begin to clog, repeated use of the file causes the workpiece itself to push the debris out from under the teeth. This process is referred to as ‘self-cleaning’.
Size
Aluminium files are usually available in lengths from 150mm (6 inches) to 300mm (12 inches).Swiss or American?
Aluminium files are American pattern files.What is a lead float?
Lead floats, or lead float files, are similar to aluminium files in all respects, except that they have their teeth spaced wider apart. They are used to file lead. A lump of lead, which should be filed with a lead float to prevent pinning.This is to provide added resistance to clogging, as lead is even softer than aluminium.
Technical Information of Hand Files
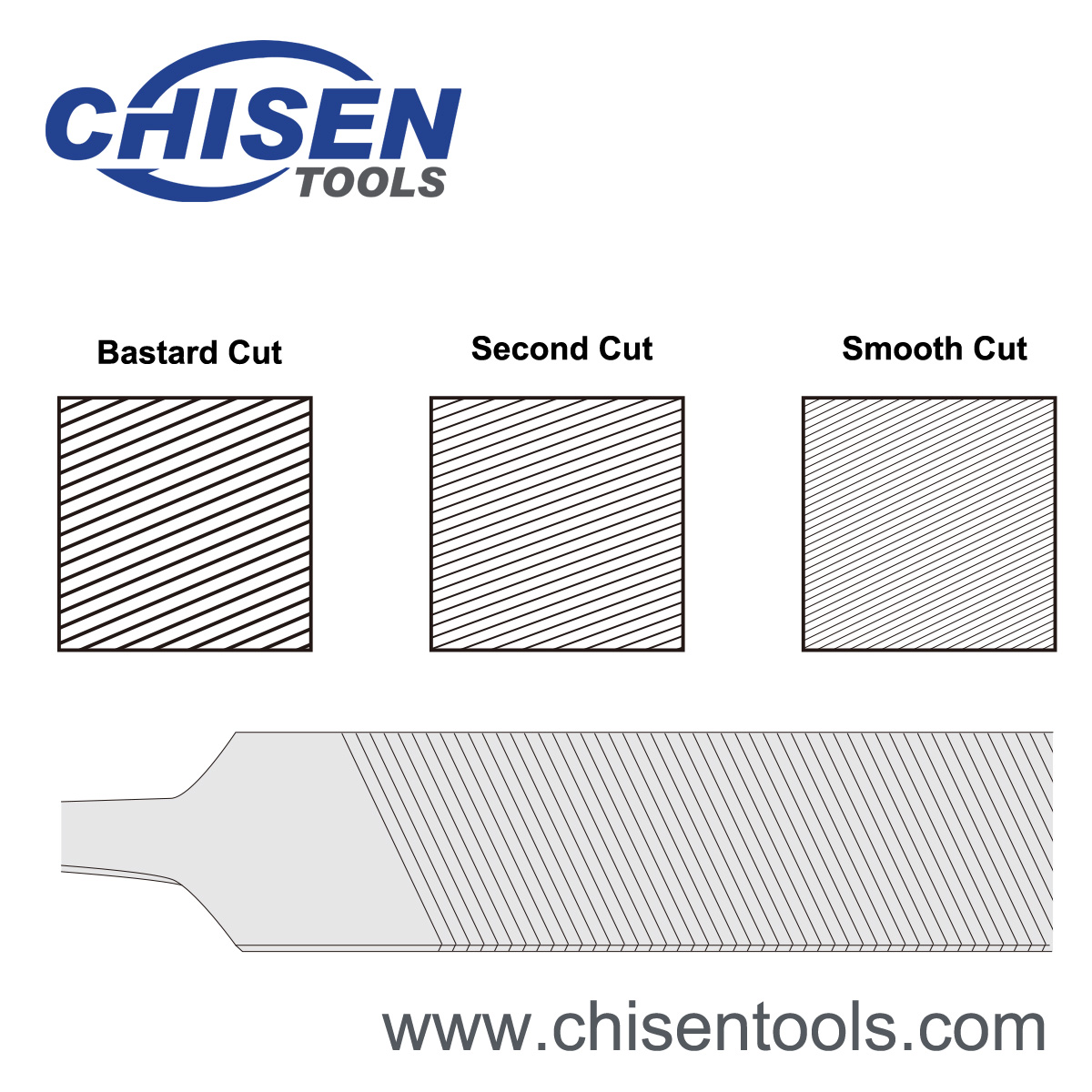
Cuts (Coarseness) of Hand Files
Bastard Cut
Bastard cut is a coarse cut for filing steels and castings.Second Cut
Second cut is a medium cut for fi ling hard metals.Smooth Cut
Smooth cut is a fi ne cut for fi ling hard metals and for finishing.Styles of Hand Files
Mill or Saw Files
Mill or saw files are used for sharpening and dressing edge tools.Machinists Files
Machinists files are used where metal must be removed rapidly.Curved Tooth Files
Curved tooth files are used for auto body repair and sheet metal work.Swiss Pattern Files
Swiss pattern files are used for fi ne fi nish work.Rasps
Rasps are used for fi ling soft metals, wood, and plastics.Teeth of Hand Files
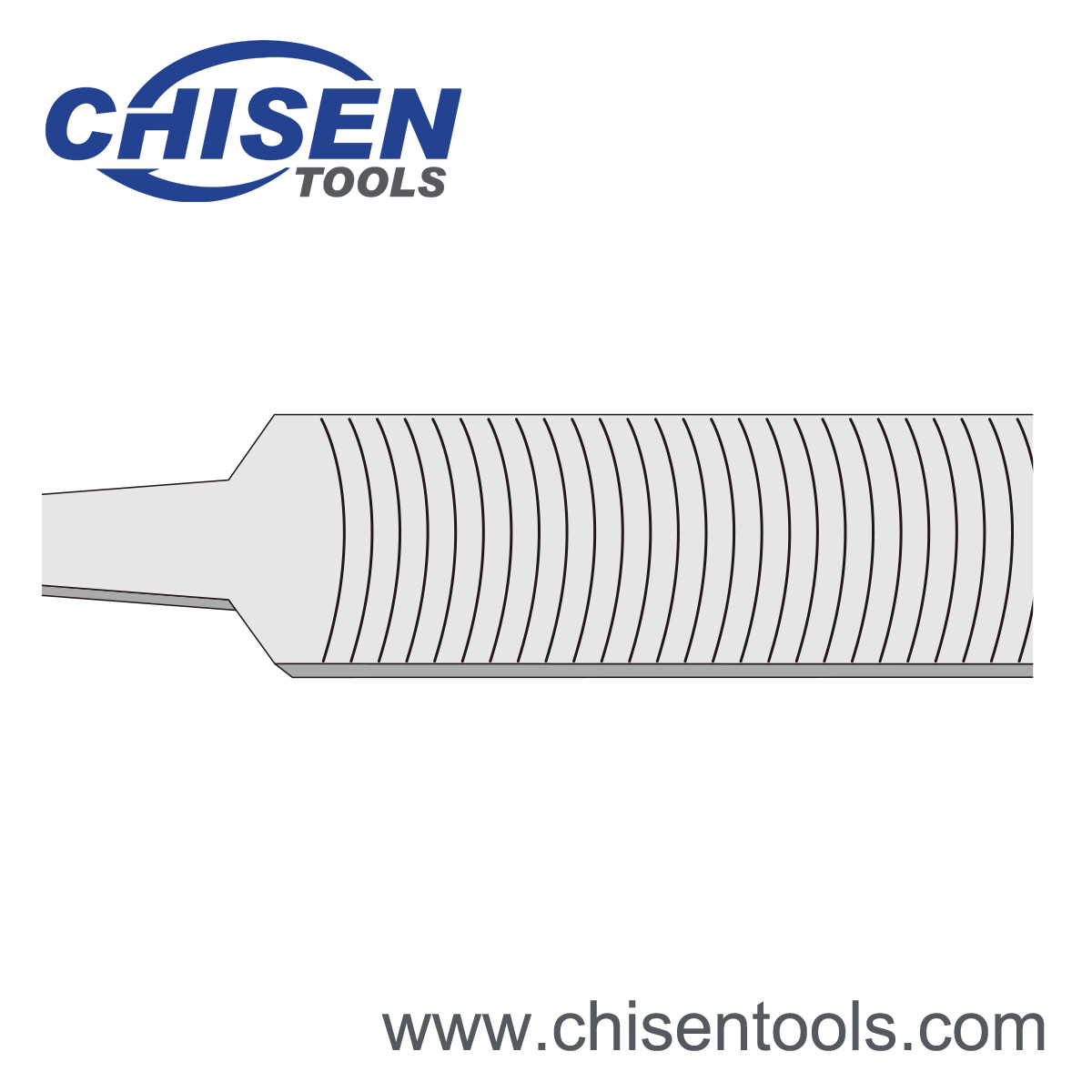
Single Cut
 Single cut is a file tooth arrangement where a series of parallel teeth run diagonally across the width of the file. It is used for sharpening saws and for finishing work.
Single cut is a file tooth arrangement where a series of parallel teeth run diagonally across the width of the file. It is used for sharpening saws and for finishing work.
- Single set of parallel, diagonal rows of teeth
- Single-cut files are often used with light pressure to produce a smooth surface finish or to put a keen edge on knives, shears or saws
Double Cut
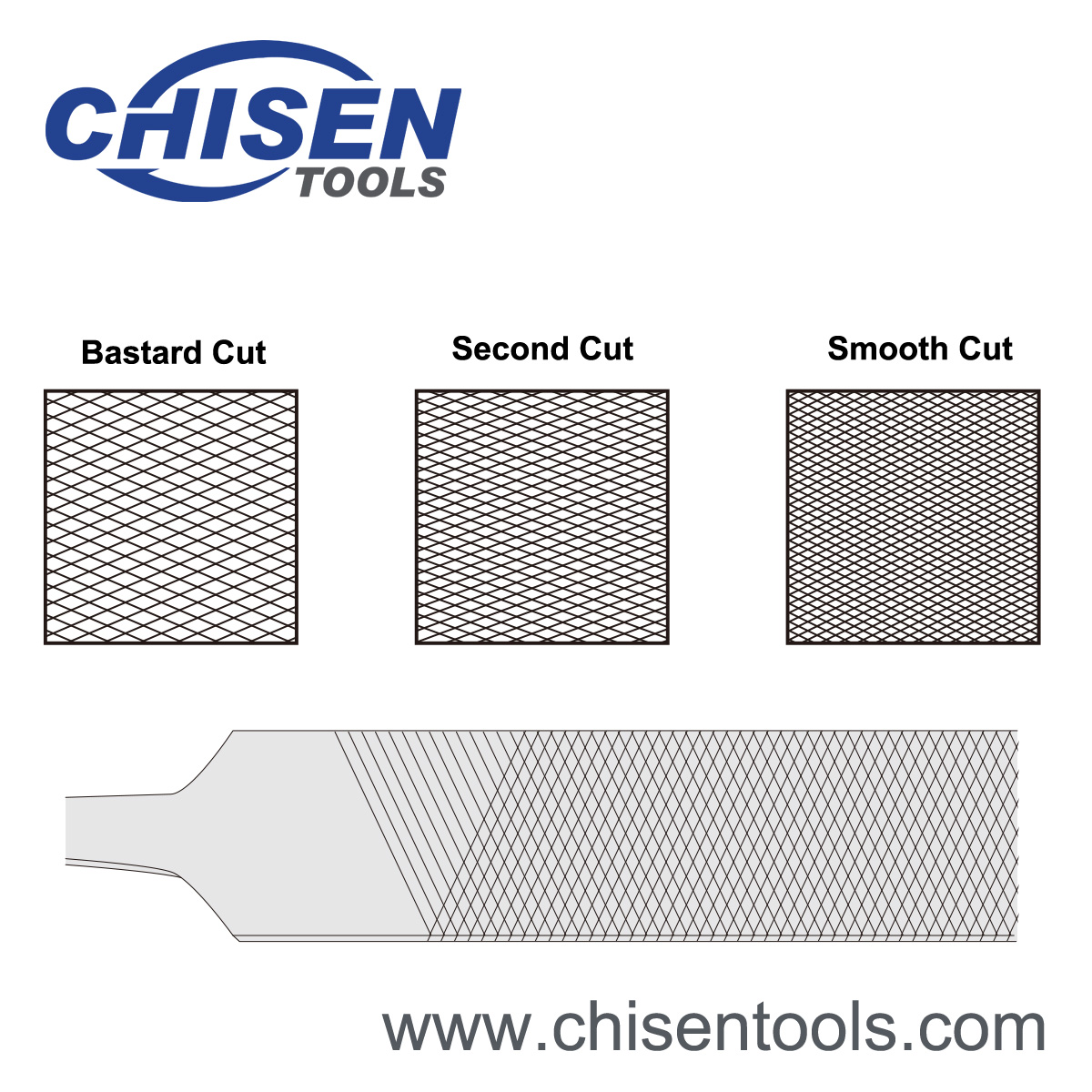 Double cut is a file tooth arrangement formed by two series of parallel teeth running diagonally across the width of the fi le with one series crossing over the other. It is used for fast stock removal.
Double cut is a file tooth arrangement formed by two series of parallel teeth running diagonally across the width of the fi le with one series crossing over the other. It is used for fast stock removal.
- 2 sets of diagonal rows of teeth
- Second set of teeth cut in opposite diagonal direction and on top of the first set
- First set of teeth is known as the overcut, second is known as upcut
- Upcut is finer than overcut
- Double-cut file is used with heavier pressure than the single-cut and removes material faster from the workpiece
Rasp Cut
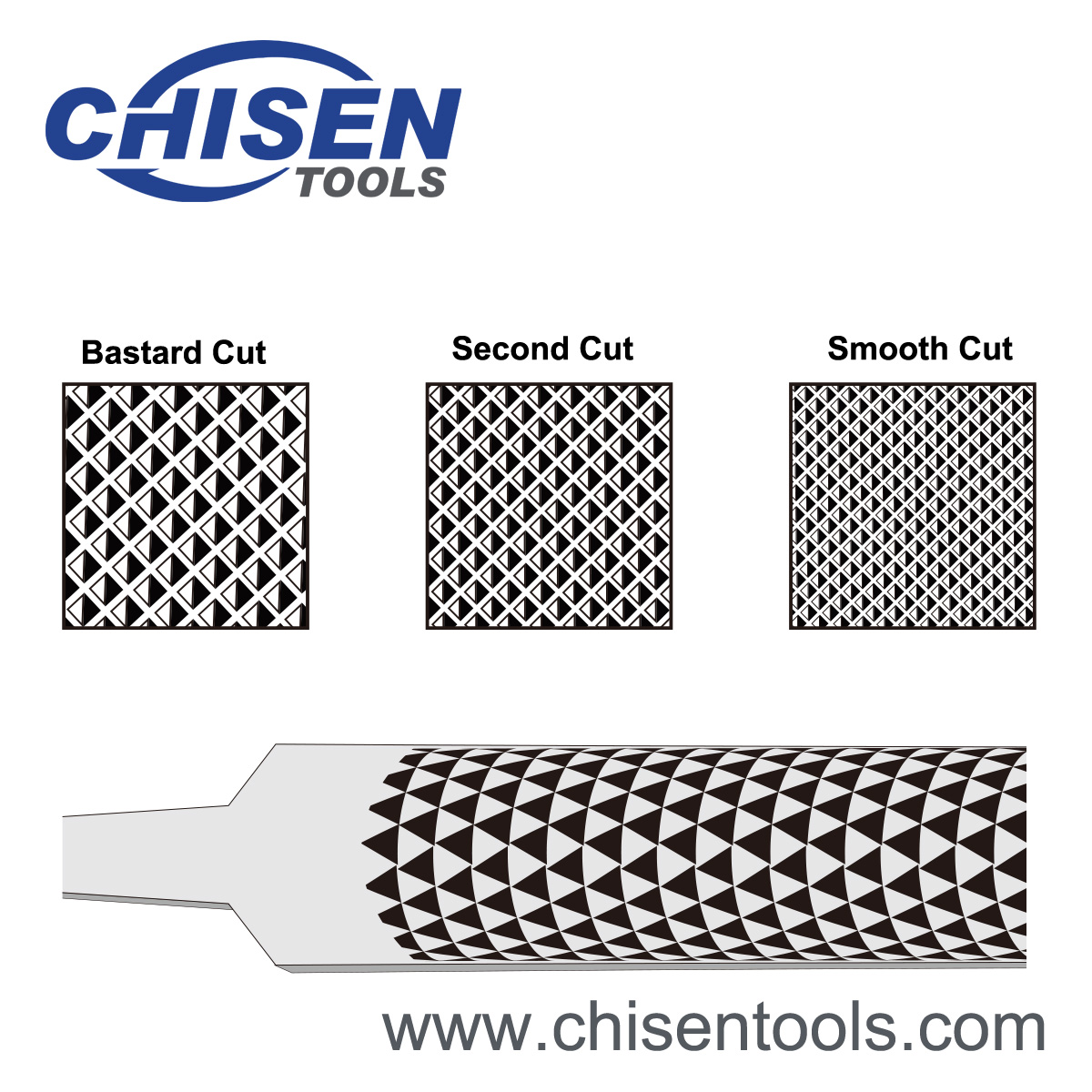 Rasp cut is a file tooth arrangement where a series of individual raised round teeth are formed by a single pointed punch tool. It is used for fast and rough cutting of wood, leather, hooves, and soft metals.
Rasp cut is a file tooth arrangement where a series of individual raised round teeth are formed by a single pointed punch tool. It is used for fast and rough cutting of wood, leather, hooves, and soft metals.
- Series of individual teeth which are formed by a single-pointed tool
- Produces a rough cut that is used primarily on wood, hooves, aluminum and lead
Curved Cut
 Curved cut is a file tooth arrangement where a series of teeth are mill cut in curved contours across the width of the fi le. It is used for fi ling soft metals, plastics and where chip removal is required.
Curved cut is a file tooth arrangement where a series of teeth are mill cut in curved contours across the width of the fi le. It is used for fi ling soft metals, plastics and where chip removal is required.
- Teeth arranged in curved contours across the file face
- Curved-cut file is normally used in automotive body shops for smoothing body panels
Length of Hand Files
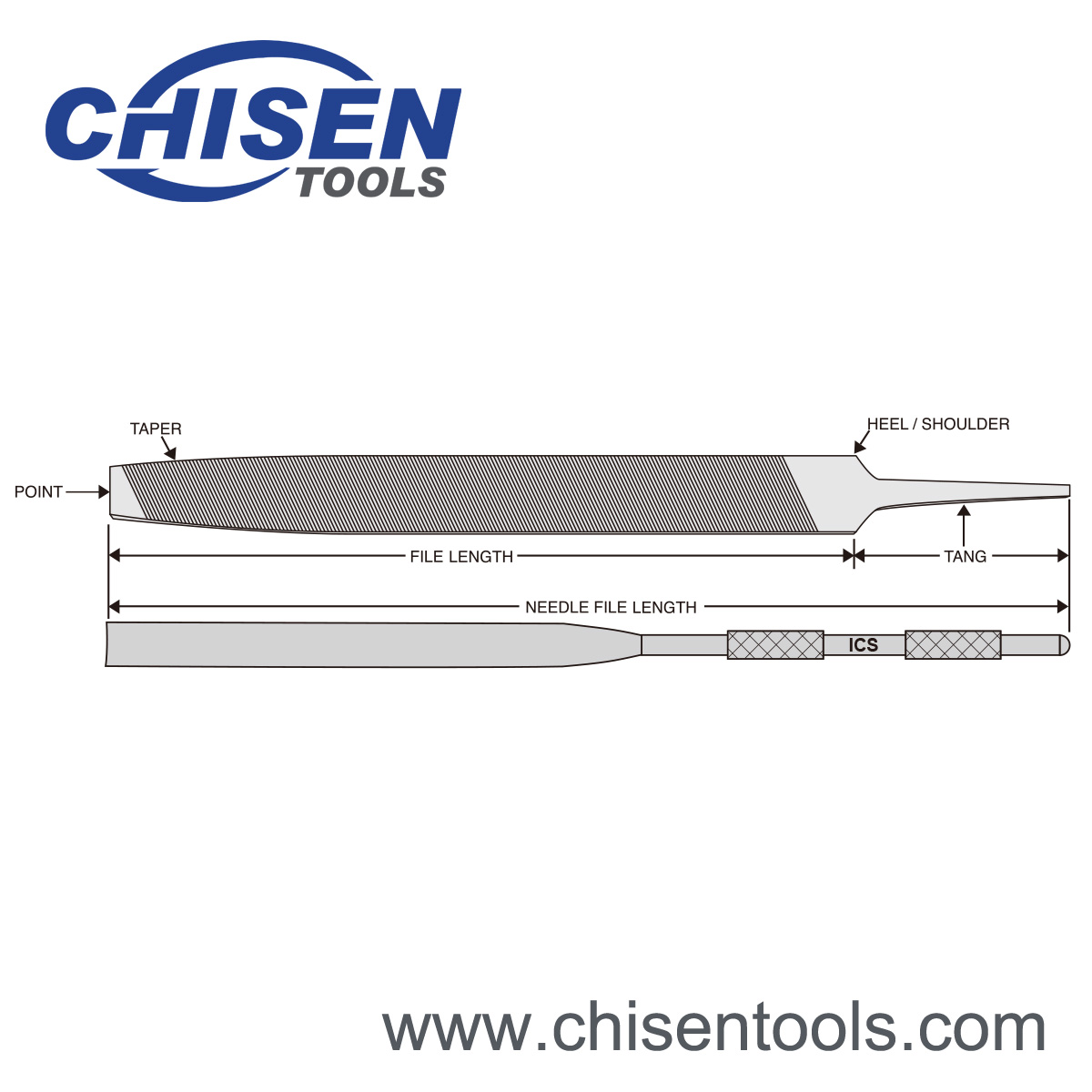 As illustrated above, American pattern file lengths do not include the tang. Swiss pattern file lengths do represent the overall length.
As illustrated above, American pattern file lengths do not include the tang. Swiss pattern file lengths do represent the overall length.




